fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic
The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. Protists are classified as animal-like protozoa plant-like algae or fungi-like molds based on.
 |
| How Do Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Differ Socratic |
ə also known as Cyanophyta are a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesisThe name cyanobacteria refers to their color from Ancient Greek κυανός kuanós blue which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacterias common name blue-green algae.

. Other eukaryotes include plants fungi and protists. All animals are eukaryotes. They appear to have originated in a. The eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells show differences among the various metabolic processes taking place in the cell.
As of 2015 and the Publication of A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms by. Similarly any wastes produced within a prokaryotic cell can quickly diffuse. At 0150 µm in diameter prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells which have diameters ranging from 10100 µm. Eukaryotes include larger more complex organisms such as plants and animals.
In eukaryotes these pieces are identified by scientists as the 60-S and 40-S. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells. The distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered to be the most important distinction among groups of organisms. Protists are eukaryotic organisms.
Weve prepared this quiz to help you test your understanding of cells and their related concepts. If you are ready to test your. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells found in domains Archaea and Bacteria. The prokaryotes small size allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly diffuse to other parts of the cell.
Eukaryotes are organisms made up of cells that possess a membrane-bound nucleus that holds DNA in the form of chromosomes as well as membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria b æ k ˈ t ɪər i ə. Eukaryotic cells can be either single-celled or have multiple cells ie unicellular or multi-cellular. Cyanobacteria s aɪ ˌ æ n oʊ b æ k ˈ t ɪər i.
2021 providing coverage of many more lineages and a. Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes are mostly unicellular organisms that lack nuclei and membrane-bound organelles. Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called eukaryotes and include plants animals fungi and protists.
If you hit more than 70 score on this test it means that you have good knowledge about the concept of cells. Instead some prokaryotes such as bacteria have a region within the cell where the genetic material is freely suspended. Animals and fungi have radically distinct morphologies yet both evolved within the same eukaryotic supergroup. The binding of transcription factor proteins to the TATA box assists in the binding of.
They all are single-celled. Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay paper or report. Classification of Protists Kingdom Protista contains a highly diverse group of organisms with few similarities between them. However this is not the case in prokaryotes that lack membrane-bound organelles.
The underlying data sets have been renewed and expanded in sync with the OrthoDB v10 release Kriventseva et al. Moreover in eukaryotes rRNA in ribosomes has four strands whereas in. Eukaryotic cells have a cell wall that protects the nucleus. The next level down of classification is into Kingdoms.
At 01 to 50 μm in diameter prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells which have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The size of a prokaryotic cell ranges from 0. Prokaryotic cells are extremely small much smaller than eukaryotic cells. In the context of TATA box it is a sequence of 5 TATAA -3 that is present in the core promoter regionTo the TATA box transcription factor proteins and histone proteins are bound.
The eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles that divide the cell into compartments. Do you think youll be able to pass this test. Singular bacterium common noun bacteria are ubiquitous mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cellThey constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganismsTypically a few micrometres in length bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth and are present in most of its habitats. Older books will teach that there are two Kingdoms Plants and Animals.
Eukaryotic Kingdoms and Prokaryotic Kingdoms. Prokaryotic cells transport their metabolites through the cytoplasm but eukaryotic cells consist of different kinds of vesicles to transport different metabolites. The most common examples of prokaryotic cells are bacteria cytoplasm blue and green algae amoeba onion peel cells plants animals fungi protozoa etc. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus while prokaryotic cells do not.
Eukaryotic organisms may be multicellular or single-celled organisms. Kingdom Protista contains all of the eukaryotic organisms that are not plants animals or fungi. This region is called the nucleoid. Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells that have nuclei.
Similarly any wastes produced within a prokaryotic cell can quickly move out. 1 m i c r o n or micrometer μ m is one-thousandth of a millimeter or one-millionth of a meter. Different metabolic processes are confined to certain cellular compartments. Synthesised polynucleotide chains enter the ER.
Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. The only organisms that are not based on the. Here we reconstructed the trajectory of genetic changes that. Examples for some eukaryotic promoters are Pribnow box TATA box GC box CAAT box etc.
A typical prokaryotic cell is of a size ranging from 01 m i c r o n s mycoplasma bacteria to 50 m i c r o n s. Protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells occurs in 80S ribosomes attached to the ER. However larger eukaryotic cells have. Hey check out this amazing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quiz that is given below.
They are capable of more advanced functions. The latest BUSCO versions introduce new functionalities for assessments of eukaryotic prokaryotic and viral data along with improvements in runtimes and user experience. This is not the case in. Furthermore prokaryotic ribosomes occur free in the cytoplasm while eukaryotic ribosomes are generally bound to the outer membrane of the nucleus and the endoplasmic.
Books produced towards the end of the last century will generally list six Kingdoms. Eukaryotic Cells The term Eukaryotes is derived from the two Greek words EU means good and Karyon means kernel which means the cell having a good nucleus. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the only kinds of cells that exist on Earth. Characteristics Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Types bacteria monerans protists fungi plants and animals Organization unicellular usually multicellular exception some protists Cell size small 01-10um larger 10-100um Membrane-bound organelles absent present Reproduction asexual asexual and sexual DNA circular linear Proteins assoc.
Prokaryotic cells consist of a single cell ie they are unicellular. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts the cell wall and the. Protein folding and transportation into various parts of the cell are maintained by. Furthermore another difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes is that the prokaryotic ribosomes consist of 30S and 50S the smaller unit and the larger unit respectively whereas eukaryotic ribosomes have smaller subunit and larger subunit as 40S and 60S respectively.
All ribosomes in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are made of two subunits one larger and one smaller. Anywhere from 200 to 10000 prokaryotic cells could fit on the head of a pin. A eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes is that the prokaryotic ribosomes are small 70 S ribosomes whereas the eukaryotic ribosomes are larger 80S ribosomes.
 |
| Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Differences Examples |
 |
| Prokaryotic Cells Kingdom Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Protista Monera Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Ppt Download |
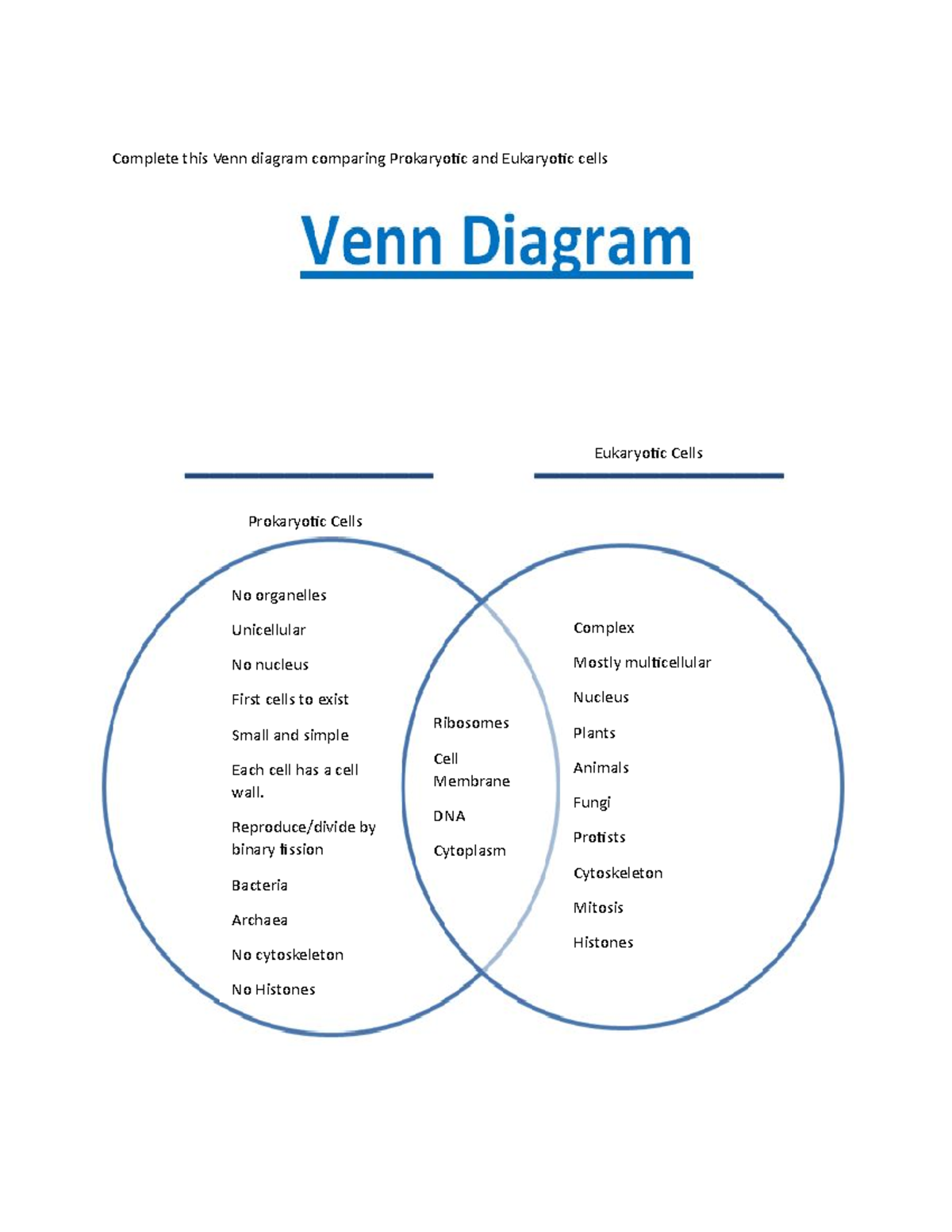 |
| Venn Diagram Student Handout Complete This Venn Diagram Comparing Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Studocu |
 |
| Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Video Khan Academy |
 |
| Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Structure And Discrete Features |
Posting Komentar untuk "fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic"